Hesperis matronalis L.
sweet rocket (dames rocket; dames'-violet)
Brassicaceae (Mustard family)
Introduction to Vascular Plants
sweet rocket (dames rocket; dames'-violet)
Brassicaceae (Mustard family)
Introduction to Vascular Plants
Species Information
General:
Perennial or biennial herb from a taproot; stems 1 to sometimes several, simple or sparingly branched, 0.5-1.3 m tall, leafy, hairy with coarse, spreading, simple or branched hairs.
Leaves:
Basal leaves soon deciduous; stem leaves lanceolate to narrowly egg-shaped, saw-toothed, 1.5-20 cm long, 0.5-4 cm wide, lower long-stalked, smaller and unstalked upwards, hairy with simple and branched hairs.
Flowers:
Fragrant; inflorescence compound, somewhat corymbiform racemes; flower stalks 3-15 mm long, ascending to spreading; petals white to rose or purple, 15-25 mm long; sepals 5-7 mm long, soft-hairy.
Fruits:
Siliques, 4-10 cm long, 1-2 mm wide, round in cross section, usually somewhat alternately contracted and expanded; seeds 3-4 mm long.
Illustration
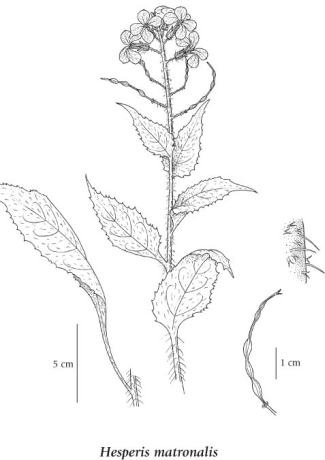
If more than one illustration is available for a species (e.g., separate illustrations were provided for two subspecies) then links to the separate images will be provided below. Note that individual subspecies or varietal illustrations are not always available.
Illustration Source: The Illustrated Flora of British Columbia
USDA Species Characteristics
Flower Colour:
Purple
Blooming Period:
Spring
Fruit/Seed characteristics:
Colour: Brown
Present from Summer to Fall
Source: The USDA
Habitat and Range
Mesic to dry roadsides, fields and disturbed areas in the lowland, steppe and montane zones; frequent in SW BC, known from Vancouver Island and the adjacent mainland, rare in SC BC, locally frequent in WC and SE BC; introduced from Eurasia.Status Information
Taxonomic Notes
In snapdragons...it has been shown that streaking of the [petals such as is found] in dame's rocket is due to jumping genes. This rather fanciful term refers to a mobile piece of DNA, which can land in the middle of another gene (in this case a pigment gene) and inactivate it (in this case causing albinism). At random intervals the jumping gene jumps out again, causing a streak of normal pigmented tissue.
Source: Griffiths and Ganders. 1983. Wildflower Genetics: A Field Guide for British Columbia and the Pacific Northwest. |
References
Griffiths, Anthony J. F. and Fred R. Ganders. 1983. Wildflower Genetics: A Field Guide for British Columbia and the Pacific Northwest. Flight Press, Vancouver.