western yew (Pacific yew)
Taxaceae (Yew family)
Introduction to Vascular Plants
Introduction
The Pacific or western yew is a small (to 15 m) evergreen coniferous trees species that is native to the Pacific Northwest of North America where is is found in Alberta, British Columbia, Alaska, Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Montana and California (Hils 2011). In British Columbia, this species is common in coastal areas and in the south-central and south-eastern regions of the province in the lowland and montane zones (Douglas et al.2000). Habitat range from "open to dense forests, along streams, moist flats, slopes, deep ravines, and coves" (Hils 2011).
The Pacific yew is on the IUCN red list of threatened species: "Native populations have been under considerable pressure from the scale of exploitation of the bark by pharmaceutical companies." (Conifer Specialist Group 1998). This species is a source of the cancer drug taxol (Hils 2011). |
Species Information
General:
Small tree 2-15 m tall, often shrubby; branches spreading to drooping in flat sprays; bark thin, with outer purplish scales over reddish to reddish-purple inner bark; male and female plants separate.
Leaves:
Needles 2-ranked, flattened, and pointed at tip, (12) 14-18 mm long, 1-2 mm broad; yellow-green and paler on lower surface.
Cones:
Fruit is a round, red, fleshy aril, 5-6 mm long, borne on the underside of the branches; pollen cones yellow, globe-shaped, 3 mm long.
Illustration
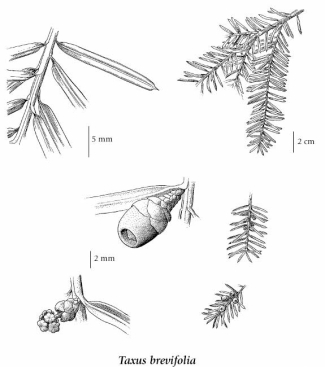
If more than one illustration is available for a species (e.g., separate illustrations were provided for two subspecies) then links to the separate images will be provided below. Note that individual subspecies or varietal illustrations are not always available.
Illustration Source: The Illustrated Flora of British Columbia
USDA Species Characteristics
Blooming Period:
Early Summer
Fruit/Seed characteristics:
Colour: Brown
Present from Summer to Fall
Source: The USDA
Ecology
The table below shows the species-specific information calculated from
original data (BEC database) provided by the BC Ministry of Forests and Range.
(Updated August, 2013)
| Site Information |
Value / Class |
||
|
Avg |
Min |
Max |
|
| Elevation
(metres) |
722 | 0 | 1890 |
| Slope
Gradient (%) |
27 | 0 | 150 |
|
Aspect (degrees) |
229 | 0 | 360 |
| Soil
Moisture Regime (SMR) [0 - very xeric; 4 - mesic; 8 - hydric] |
4 | 0 | 8 |
| Modal
Nutrient Regime
Class |
C | ||
| #
of field plots species was recorded in: |
1879 | ||
| Modal
BEC Zone Class |
ICH | ||
|
All BEC Zones (# of stations/zone) species was recorded in |
CDF(83), CWH(543), ESSF(30), ICH(1158), IDF(16), MH(8), MS(11) | ||
|
Source:
Klinkenberg 2013
|
|||